Bridging deep learning and modular synthesis: A real-time AI-based Eurorack synthesizer for expressive sound design.
The Neurorack project pioneers the integration of deep learning models directly into the tactile, performance-oriented world of Eurorack modular synthesizers. Developed at IRCAM within the ACIDS group, the Neurorack enables real-time, descriptor-driven sound synthesis using AI models running entirely on embedded hardware — no laptop required.
The spirit of The Neurorack lies in its modularity not just physically, but also computationally: it supports model switching, allowing different AI models to be trained and embedded for various synthesis goals. This means users can adapt the module to generate entirely different types of sounds depending on the trained model, all within the same hardware platform.
This page documents the instrument’s philosophy, design challenges, technical implementation, creative potential, and ongoing evolution.
The Challenge: Real-Time AI in a Tiny Box
Modern deep generative models can produce incredibly realistic audio, but often require significant computational power (GPUs, large memory) and processing time, making them unsuitable for the strict constraints of musical instruments, especially compact Eurorack modules.
The Neurorack tackles this challenge head-on:
- Real-Time Performance: Achieving low-latency audio generation suitable for live performance and interaction.
- Embedded Constraints: Operating within the limited power, size (3U height, variable HP width), and computational resources of the Eurorack format.
- Musical Expressivity: Providing intuitive, high-level control over complex timbres using standard Control Voltage (CV) and Gate signals.
Our design philosophy centers on balancing model accuracy with lightweight efficiency and meaningful user interaction.
Core Technology
Hardware: NVIDIA Jetson Power in 11hp
The computational core is the NVIDIA Jetson Nano, chosen for its balance of:
- Quad-core ARM CPU & 128-core Maxwell GPU (CUDA-enabled)
- 4GB LPDDR4 RAM
- Compact size and energy efficiency
This allows us to run optimized deep learning models directly within the Eurorack module. The hardware module itself occupies 11hp width in a standard 3U Eurorack case.
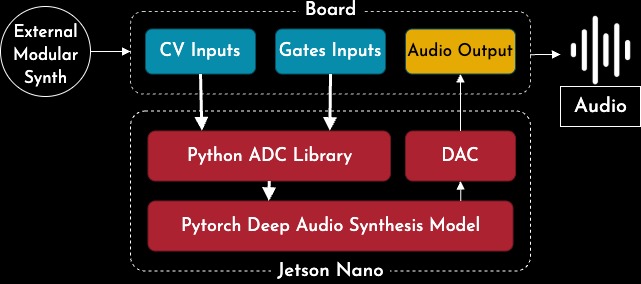
The Neurorack is a deep learning-driven instrument that incorporates advanced audio synthesis techniques within a modular synthesizer environment. It’s composed of two main parts: a hardware module that interfaces with other Eurorack systems via Control Voltage (CV) and Gate inputs, and an embedded Jetson Nano board that handles real-time audio computation.
The hardware is responsible for capturing and interpreting CV/Gate signals, while the Jetson Nano processes those in real time using a deep neural network to generate audio. This modular split keeps interaction intuitive and performance-friendly, while offloading the heavy lifting to the embedded AI system.
Sound Synthesis: Descriptor-Driven Sinc-NSF (First Model)
This model specializes in generating impact sounds – complex, transient-rich, often cinematic sounds like deep kicks or resonant hits, which are notoriously difficult to create convincingly with traditional synthesis methods.
- Dataset: Trained on a curated dataset of 3,500 high-quality impact samples (44.1kHz) sourced from Splice, normalized and trimmed.
- Model: Uses a highly adapted Sinc-NSF (Neural Source-Filter) model. Inspired by speech synthesis and DSP, this model separates sound into harmonic and noise components, generated in a single pass for real-time efficiency. Key features include:
- Descriptor Conditioning: Synthesis is controlled by 7 perceptual audio descriptors calculated frame-by-frame: Loudness (RMS), Percussivity (ZCR), Brightness (Centroid), Tone (Roll-off), Richness (Bandwidth), Noise (Flatness), and Pitch ($f_0$).
- SincNet Filters: Employs trainable, DSP-inspired Sinc filters for efficient and interpretable spectral shaping, replacing generic convolutions.
- Spectral Loss: Optimized using a multi-resolution spectral loss to capture both transient details and overall timbral character.
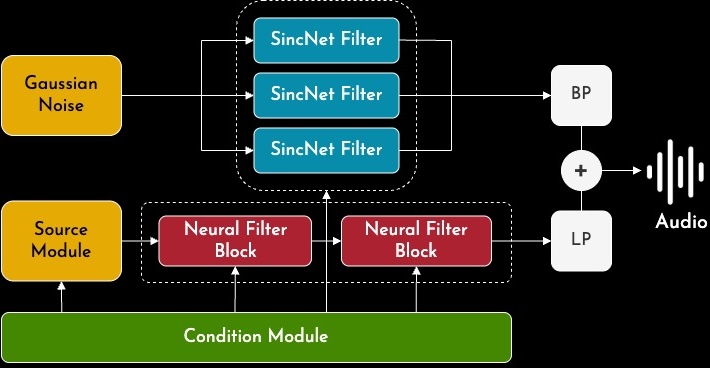
- Descriptor Generation (VAE): To explore the timbral space and generate new sounds, a Variational Autoencoder (VAE) was trained on the descriptor curves from the dataset. This allows sampling or interpolating in a low-dimensional latent space to create novel, coherent descriptor sets that drive the Sinc-NSF model.
Interface & Interaction: Hands-On AI Control
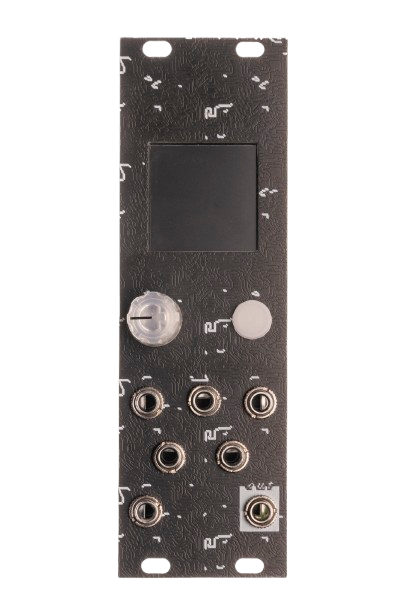
The Neurorack faceplate provides immediate tactile control, integrated seamlessly into the modular workflow:
- 1.3-inch OLED Display: Visual feedback for parameters, modes, and navigation.
- Rotary Encoder + Push Button: For menu navigation and parameter adjustments.
- 2 Gate Inputs: Triggering events.
- 4 CV Inputs: Modulating synthesis parameters.
- 1 Mono Audio Output: Standard Eurorack level output.

CV & Gate Mapping for Creative Expression
Standard Eurorack CV ($+/- 5V$) and Gate ($> 2.5V$ ON) signals control the AI model in musically meaningful ways:
- Gate 1 (Trigger): Initiates sound generation. Essential for rhythmic sequencing.
- Gate 2 (Freeze Loop): Activates a granular buffer, capturing and looping a short segment (~50-100ms) of the output for textural effects as long as the gate is high.
- Creative Use: Create stuttering effects, evolving pads, or rhythmic variations by gating the buffer.
- CV 1 (Descriptor Interpolation): Morphs between two predefined sets of sound descriptors ($\mathbf{F}_1, \mathbf{F}_2$). A voltage from -5V to +5V sweeps the interpolation weight $\alpha$ from 0 (fully $\mathbf{F}_1$) to 1 (fully $\mathbf{F}_2$).
- Creative Use: Use an LFO or envelope on CV1 to create smooth timbral transitions, evolving textures, or dynamic shifts between drastically different impact sounds.
- CV 2 (Descriptor Scrubbing): Navigates through a small buffer of recent descriptor frames, similar to granular time-stretching but applied to the control parameters.
- Creative Use: Modulate with a slow LFO or sequence to create evolving, non-repetitive timbres. Use faster modulation for glitchy, granular-like textural effects on the sound’s character.
- CV 3 (Transient Shaping): Dynamically adjusts the impact’s attack and perceived punch by gently scaling the RMS (loudness) and Spectral Bandwidth descriptors.
- Creative Use: Control the “hardness” or “softness” of the impact using velocity CV from a sequencer or keyboard. Shape percussive sounds from sharp clicks to booming hits.
- CV 4 (Stochastic Variation): Introduces controlled randomness (0-20% intensity based on CV) to selected descriptors, adding subtle organic variations.
- Creative Use: Add “human” feel to repetitive sequences. Generate slight timbral shifts to prevent sounds from becoming static. Increase for more chaotic, unpredictable textures.
Listen
Audio Demo: A track composed entirely using impact sounds generated by the Neurorack.
Video Teaser:
Development & Evolution
V1 Prototype: Proof of Concept
The first version successfully demonstrated real-time embedded AI synthesis but had limitations:
- Exposed cabling and external power (not ideal for robust Eurorack use).
- Limited CV interaction responsiveness in early software iterations.
- Model “burn-in” required on startup.
- Fixed descriptor sets required code changes for customization.
V2 Prototype: Refinements & Future Directions
Developed with Corentin Vercoustre, V2 addressed key issues:
- Redesigned Faceplate: Sleeker, more robust, better internal wiring.
- Improved Stability: Internalized connections for better reliability.
- New Model Integration: Work began on integrating FRAVE, a different generative model (from Chapter 4 of the PhD) focused on continuous timbral control via latent space exploration.
- Future: Ongoing work focuses on enhancing responsiveness, parameter mapping, and exploring new models. V2 (with FRAVE) aims for presentation at Sónar+D 2025.
Community Recognition & Showcases
Neurorack has been presented at major industry events and recognized by the tech community:
NVIDIA Jetson Project of the Month: Recognized for innovative use of the Jetson platform. (Community Project Page)
- Showcases:
- IRCAM Manifeste (Paris): Presented to the label Raster-Noton.
- Superbooth (Berlin): Dedicated booth at one of the world’s largest synthesizer trade show.
- SynthFest France (Nantes) (Video Link Placeholder)
- 📰 Media Coverage: Featured on Synthtopia, Sonic State (Talk Video Link Placeholder), Keyboards.de, Matrixsynth, Geeky Gadgets.
Learn More & Get Involved
- 📄 Scientific Publication: Devis et al., “Real-Time Embedded AI for Modular Synthesis: The Neurorack Project”, EPFL, 2022 (Detailed paper).
- 💾 GitHub Repository: acids-ircam/neurorack (Code, Schematics - Note: May reflect V1 status).
- 💡 NVIDIA Developer Blog Post: In-depth feature on the project.
Credits
A collaborative project by:
- Ninon Devis (IRCAM / Native Instruments)
- Martin Vert (Hardware V1)
- Corentin Vercoustre (Hardware V2)
- Valentin Lageard (Hardware V2)
- Philippe Esling